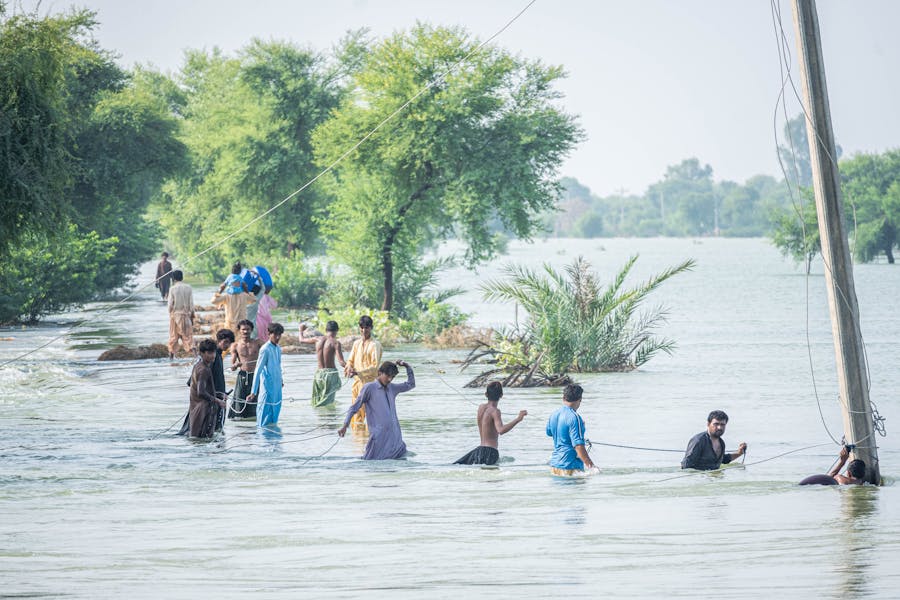
Floods are among the most frequent and destructive natural disasters, impacting lives, property, and ecosystems worldwide. While every region faces some flooding risk, specific areas are disproportionately affected due to geographical, climatic, and human factors. Identifying where floods mainly occur and understanding their underlying causes are crucial for disaster preparedness and mitigation.
Low-lying regions, river basins, and coastal areas are particularly vulnerable, with countries like Bangladesh, India, and the United States frequently experiencing floods. Heavy rainfall, river overflow, and storm surges exacerbate the situation. Urbanization, deforestation, and poor land management further contribute to the frequency and intensity of flooding.
This article explores the regions most prone to flooding, delves into the causes and impacts, and provides actionable strategies for risk reduction. Whether you live in a flood-prone area or want to understand this phenomenon, this comprehensive guide offers valuable insights.
Where Do Floods Mostly Occur?
Floods mainly occur in low-lying areas, river basins, and coastal regions, where factors like heavy rainfall, river overflow, and storm surges play a significant role. Countries such as Bangladesh, India, and the U.S. face frequent flooding due to monsoons, hurricanes, and poor drainage systems. Understanding flood-prone areas and implementing preparedness strategies are crucial for mitigating risks and reducing damage.
Flood-Prone Regions: A Global Perspective
Floods are a universal phenomenon, but some areas experience them more frequently and severely than others. These areas often share common geographical and climatic characteristics, such as low-lying, near rivers, or near coasts. Additionally, urban centers with inadequate drainage systems are increasingly becoming flood hotspots due to rapid urbanization.
Asia
Asia is the most flood-prone continent, with countries like Bangladesh, India, and China experiencing regular flooding. The monsoon season brings heavy rainfall, overwhelming rivers like the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Yangtze. Coastal cities, including Mumbai and Shanghai, also face risks from storm surges and rising sea levels.
North America
The Mississippi River basin is infamous in North America for its recurrent flooding. Heavy rainfall and snowmelt from the Rockies cause the river to overflow, affecting millions. Coastal areas like Florida and Louisiana are also at risk due to hurricanes and storm surges.
Europe
Europe faces significant flooding along major rivers such as the Danube, Rhine, and Thames. Additionally, low-lying countries like the Netherlands, which lies below sea level, are particularly vulnerable. Heavy rainfall, snowmelt, and rising seas contribute to Europe’s flood challenges.
Africa and South America
In Africa, the Nile River basin frequently experiences flooding due to seasonal rains. West Africa also suffers from flash floods during intense rainy seasons. In South America, the Amazon basin faces annual flooding, affecting wildlife and communities. Coastal cities in Brazil are similarly at risk due to storm surges.
Urban Areas
Flooding in cities has become a growing concern. Urbanization replaces natural landscapes with impervious surfaces, reducing water absorption. Cities like Jakarta, Bangkok, and Houston face recurring urban floods due to poor drainage systems and extreme weather events.
Causes of Floods in Prone Areas
Heavy Rainfall
Regions experiencing prolonged or torrential rains often face devastating floods. For example, the monsoon season in Southeast Asia causes widespread flooding every year. Intense downpours overwhelm rivers, drainage systems, and urban infrastructure. Countries like India and Bangladesh are prime examples of areas where heavy rainfall leads to catastrophic flooding.
River Overflow
Riverine flooding occurs when rivers overflow their banks, inundating surrounding areas. Major river systems such as the Mississippi, Amazon, and Nile are particularly prone to this. Seasonal snowmelt and heavy rains swell these rivers, causing widespread damage. Low-lying agricultural lands near rivers are often the most affected, leading to food shortages and economic losses.
Coastal Flooding
Coastal areas are susceptible to floods caused by hurricanes, cyclones, and storm surges. Rising sea levels have further exacerbated this problem. For instance, the southeastern United States, including Florida and Louisiana, frequently experiences coastal flooding during hurricane season.
Snowmelt
Springtime snowmelt significantly contributes to flooding in mountainous regions. Areas like the Rockies in North America and the Himalayas in Asia see rivers swollen by melting snow, often leading to downstream flooding. This type of flooding is particularly dangerous because it can occur rapidly and without much warning.
Urbanization and Poor Drainage
Rapid urbanization has made cities increasingly vulnerable to floods. Replacing natural vegetation with impervious surfaces like concrete reduces water absorption. An inadequate drainage system creates conditions ripe for urban flooding during heavy rains. Cities like Jakarta and Mumbai are prime examples.
Most Flood-Prone Regions Globally
- Asia:
- Monsoon rains and rivers like the Yangtze, Brahmaputra, and Ganges.
- Coastal areas in countries such as India and the Philippines face cyclones.
- North America:
- The Mississippi River basin frequently floods due to rain and snowmelt.
- Coastal areas, including Florida and the Gulf Coast, are vulnerable to hurricanes.
- Europe:
- Low-lying areas near rivers like the Rhine and Danube.
- Countries like the Netherlands use extensive flood management systems to cope.
- Africa:
- Seasonal rains cause floods in the Nile and Niger River basins.
- Coastal areas face risks due to rising seas and storm surges.
- South America:
- The Amazon basin experiences annual flooding, affecting wildlife and communities.
- Coastal cities like Rio de Janeiro face urban flooding.
Impacts of Flooding in High-Risk Areas
Flooding severely and widely impacts human life, economies, and the environment.
Economic Impacts: Floods result in billions of dollars in damages annually. Infrastructure, homes, and businesses are often destroyed, leaving communities in financial ruin. Agriculture is particularly vulnerable, as floods can wash away crops, leading to food shortages and price hikes.
Social Impacts: Communities face displacement, leading to overcrowded shelters and loss of livelihoods. Flood victims often suffer from psychological trauma due to the sudden loss of homes and loved ones.
Health Risks: Stagnant floodwaters become breeding grounds for diseases like malaria and dengue. Waterborne illnesses such as cholera and typhoid also spread rapidly in flood-affected areas.
Environmental Impacts: Floods disrupt ecosystems, displacing wildlife and altering habitats. Soil erosion and sedimentation can harm rivers and wetlands.
Mitigating Flood Risks in Vulnerable Areas
Floodplain Management: Planning land use effectively can minimize flood risks. Restricting construction in flood-prone areas and preserving natural floodplains can help reduce damage.
Improved Infrastructure: Building efficient drainage systems in urban areas can mitigate the impact of heavy rains. Upgrading levees and dams also help control riverine flooding.
Early Warning Systems: Technological advancements allow for accurate weather predictions and flood warnings. Governments and communities must invest in systems that provide timely alerts.
Reforestation and Ecosystem Restoration: Planting trees stabilize soil, reduces runoff, and helps control floods. Restoring wetlands can act as natural buffers, absorbing excess water.
Community Education: Educating the public about flood risks, evacuation plans, and safety measures can save lives and reduce damage during disasters.
Conclusion
Floods predominantly occur in low-lying areas, river basins, and coastal regions, driven by natural factors like rainfall, snowmelt, storm surges, and human-induced factors like urbanization and deforestation. Understanding these flood-prone areas and the underlying causes is crucial for effective disaster preparedness. By adopting strategies such as floodplain management, improved infrastructure, and community education, we can mitigate the devastating impacts of flooding. Protecting vulnerable areas and building resilience are essential steps toward minimizing flood-related disasters.
FAQ’s
Where do floods happen most often?
Floods commonly occur in low-lying areas, river basins, and coastal regions. Countries like Bangladesh, India, and the U.S. are prone to flooding.
How can urban flooding be prevented?
Urban flooding can be mitigated by improving drainage systems, adopting sustainable urban planning, and increasing green spaces to absorb water.
What is riverine flooding?
Riverine flooding occurs when rivers overflow due to heavy rainfall, snowmelt, or dam breaches.
Why is Bangladesh prone to flooding?
Bangladesh is prone to flooding due to its location at the confluence of major rivers, low elevation, and frequent monsoons.
What are the health impacts of floods?
Floods increase the risk of waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid, and malaria due to stagnant water and poor sanitation.