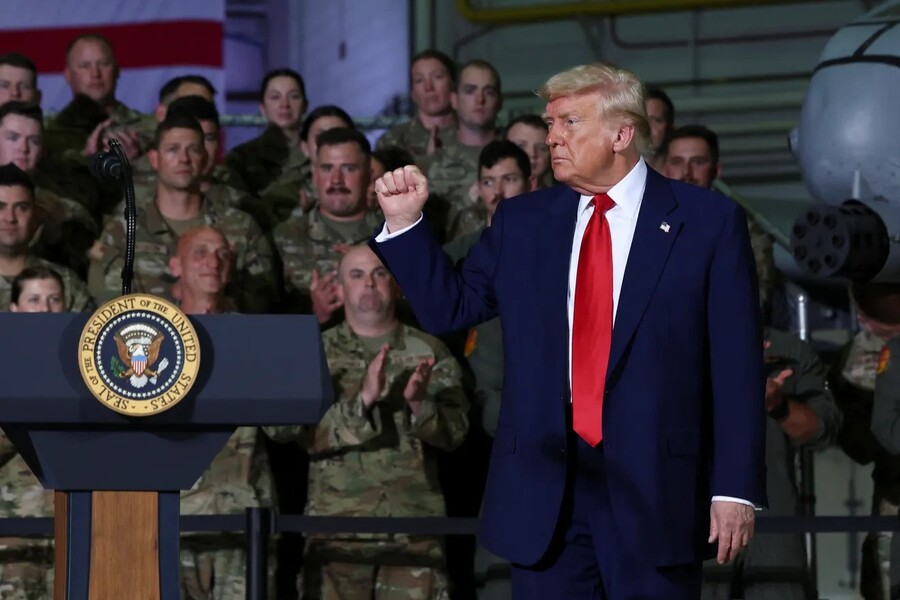
In a significant legal and political victory for former President Donald Trump, the U.S. Supreme Court has allowed the reinstatement of a controversial ban on transgender individuals serving in the military, pending the outcome of ongoing court challenges. The move, which took effect on May 6, reignites a contentious debate over military policy, civil rights, and the treatment of LGBTQ+ individuals in federal institutions.
A Deeply Divided Court Greenlights Policy
The Supreme Court’s decision came in response to an emergency request by Trump’s legal team after lower federal courts had blocked the policy. While the court offered no detailed explanation—a common practice for emergency appeals—its three liberal justices, Sonia Sotomayor, Elena Kagan, and Ketanji Brown Jackson, publicly dissented, saying they would have denied the administration’s request.
For Trump and his supporters, the ruling is a validation of his longstanding efforts to reshape the military around what he calls a focus on “readiness and lethality.” White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt echoed this sentiment, declaring the decision a “massive victory” and accusing prior administrations of prioritizing “woke gender ideology” over national defense.
Legal and Human Rights Advocates Sound the Alarm
The policy has been roundly criticized by LGBTQ+ advocacy groups, military readiness experts, and civil rights organizations, who argue that the ban is rooted not in evidence but in prejudice. Lawyers for the plaintiffs—including Lambda Legal and the Human Rights Campaign Foundation—called the Supreme Court’s move a “devastating blow” for thousands of transgender service members and a temporary endorsement of discrimination.
“By allowing this discriminatory ban to take effect while our challenge continues, the Court has temporarily sanctioned a policy that has nothing to do with military readiness and everything to do with prejudice,” the legal coalition said in a joint statement.
The ban prevents transgender individuals from enlisting in the military, halts military coverage for certain gender-affirming medical treatments such as hormone therapy and surgery, and creates conditions that could lead to the removal of currently serving transgender personnel.
Lower Courts Previously Rejected the Ban
Prior to the Supreme Court’s intervention, lower courts had issued multiple rulings against the policy. On March 27, U.S. District Judge Benjamin Settle in Seattle issued a preliminary injunction, asserting that the government’s arguments lacked credible evidence and failed to justify the ban.
“The government’s arguments are not persuasive, and it is not an especially close question on this record,” Settle wrote in his opinion, undercutting claims that transgender service harms military readiness.
Similarly, U.S. District Judge Ana Reyes in Washington, D.C., offered a blistering critique in a parallel case, calling the administration’s reasoning “soaked with animus and dripping with pretext.” Her order temporarily blocking enforcement of the ban is currently under review by the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals.
Trump’s Executive Order and Its Broader Impact
The policy stems from a 2017 executive order issued by then-President Trump, who argued that transgender identities were incompatible with military discipline and cohesion. The Pentagon subsequently revised its protocols, denying enlistment to transgender individuals and ending funding for many forms of gender-affirming care, with plans to discharge those already serving.
Critics argue that this stance not only ignores scientific evidence but also undermines the contributions of thousands of service members. According to estimates, between 10,000 and 14,000 transgender individuals currently serve in the U.S. military, with approximately 1,000 having received gender-related medical treatment.
A Pentagon-commissioned study released during the Obama administration concluded that allowing transgender people to serve openly posed minimal financial cost and had no negative impact on unit readiness or cohesion.
Why This Matters
The Supreme Court’s decision to allow the policy to proceed has wide-reaching implications:
- For the military, it disrupts the careers and lives of thousands of current and prospective service members.
- For transgender rights: It sends a chilling message about the legal protections available to marginalized communities.
- For future policy: It signals how much executive power can influence deeply personal and societal issues, particularly under a deferential Supreme Court.
The Department of Justice continues to defend the policy, insisting that it aligns with military readiness goals and reflects expert judgment. They also argue that the current ban is legally consistent with a previous version upheld by the court during Trump’s first term. However, lawyers for the plaintiffs counter that the new policy is significantly more expansive and harmful.
What Comes Next?
The policy’s long-term fate remains uncertain. The court challenges continue to move through the federal appellate system, and eventual arguments on the merits may yet bring the issue back before the Supreme Court for a full hearing. For now, though, the ban remains in place.
This ruling adds yet another chapter to the broader national conversation about LGBTQ+ rights, inclusion in the armed forces, and the balance between national security and individual freedoms.