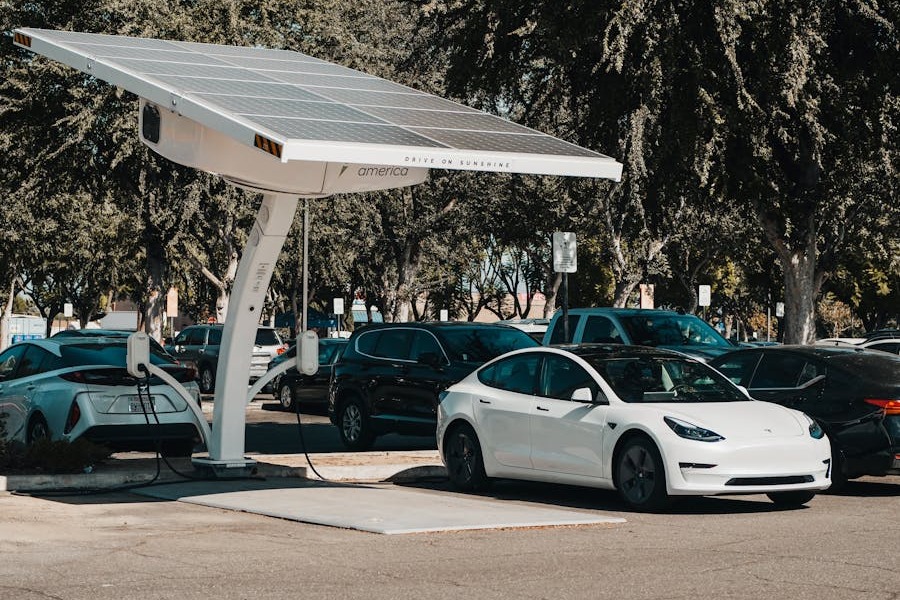
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping the global transportation landscape, promising a future free from dependence on fossil fuels. But are electric vehicles better for the environment? This question has become pivotal in discussions about sustainability and climate change. EVs are often championed as a cleaner, greener alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, with the potential to cut greenhouse gas emissions and reduce air pollution.
However, the environmental impact of EVs is more complex than it may seem. From the energy-intensive manufacturing of batteries to the sourcing of electricity used for charging, the entire lifecycle of an EV needs to be evaluated. Are the environmental benefits of EVs significant enough to justify their adoption? How do factors like renewable energy integration, battery recycling, and governmental support influence the equation?
This comprehensive article will delve into the many facets of EVs’ environmental impact. By examining their benefits, challenges, and the broader context of their adoption, we aim to answer the critical question: Are electric vehicles truly better for the environment?
Are electric vehicles better for the environment?
Yes, electric vehicles are better for the environment in several ways. They eliminate tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing urban air pollution and greenhouse gases. While battery production and energy sources for charging can present challenges, ongoing advancements in renewable energy and recycling make EVs increasingly sustainable. When powered by clean energy, EVs offer a clear path toward a greener future.
The Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles have gained a reputation as a sustainable alternative to traditional vehicles, but a full understanding of their environmental impact requires a nuanced perspective. Let’s explore how EVs influence the environment across their lifecycle:
Tailpipe Emissions: A Breath of Fresh Air
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them a game-changer for reducing city air pollution. Unlike ICE vehicles, which emit harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, EVs contribute to cleaner air and fewer respiratory diseases. This represents a significant benefit for urban areas plagued by smog and air quality issues.
Production Challenges: The High Cost of Green
The production of EV batteries, particularly lithium-ion ones, is resource-intensive. Mining materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel often lead to deforestation, water contamination, and disruption of local ecosystems. Moreover, battery manufacturing consumes large amounts of energy, increasing an EV’s initial carbon footprint. However, advances in technology and recycling are gradually reducing these environmental costs.
Energy Sources for Charging
An EV’s sustainability depends heavily on how its electricity is generated. In regions where power grids rely on coal or natural gas, EVs’ environmental advantages can diminish. Conversely, EVs charged with renewable energy sources like wind, solar, or hydroelectric power significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Lifecycle Emissions: The Bigger Picture
EVs generally have a lower carbon footprint than ICE vehicles over their entire lifespan. Studies show that despite the emissions from battery production, EVs’ operational efficiency and lack of tailpipe emissions reduce overall emissions.
Recycling and Circular Economy
Recycling batteries is critical to reducing the long-term environmental impact of EVs. Efforts to recover valuable materials like lithium and cobalt are essential to creating a circular economy, minimizing the need for mining, and reducing waste.
How Electric Vehicles Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
EVs: The End of Tailpipe Emissions
Electric vehicles do not rely on combustion engines, a major source of greenhouse gases. Traditional cars emit large amounts of carbon dioxide during operation, contributing to global warming. EVs, by contrast, are emissions-free at the point of use. This advantage alone makes them an attractive option for combating climate change.
Renewable Energy: Unlocking EV Potential
The real environmental benefits of EVs are unlocked when they are powered by renewable energy. Charging an EV using solar, wind, or hydroelectric power can lead to near-zero operational emissions. Countries investing in greener grids—such as Norway—demonstrate how EVs and renewable energy can transform transportation into a sustainable system.
Comparing Emissions: ICE vs. EVs
Lifecycle emissions provide the most accurate comparison of EVs and ICE vehicles. While producing EVs generates more emissions initially, these are offset during use. Over time, EVs powered by clean electricity emit far less CO2 than traditional cars. For example, an EV driven for 100,000 miles typically emits 50% fewer greenhouse gases than a similar gasoline-powered vehicle.
Policy Incentives for EVs
Governments worldwide are driving EV adoption through tax credits, subsidies, and emissions regulations. These policies make EVs more affordable and encourage automakers to innovate and reduce production emissions.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles
- Cleaner Air in Cities
- EVs improve urban air quality by eliminating nitrogen oxides and particulate matter pollutants.
- Reducing smog and respiratory diseases leads to significant public health benefits.
- Energy Efficiency
- EVs are far more energy-efficient than ICE vehicles.
- Electric motors convert 60–80% of the energy into motion, compared to just 20–30% for gasoline engines.
- Cost Savings Over Time
- Lower fuel costs and minimal maintenance requirements make EVs cost-effective in the long run.
- Support for Renewable Energy Goals
- EVs enable grid stability by acting as mobile energy storage units.
- They complement efforts to shift energy systems toward renewables.
- Reduced Noise Pollution
- EVs operate silently, reducing noise pollution in residential and urban areas.
Challenges in EV Production and Adoption
Electric vehicles, despite their advantages, face several hurdles that complicate their widespread adoption:
Raw Material Extraction
The extraction of lithium, cobalt, and nickel can have severe environmental and social consequences. Mining often leads to habitat destruction, water scarcity, and human rights abuses. Sustainable mining practices and ethical sourcing are crucial to addressing these issues.
Battery Manufacturing
Producing EV batteries requires large amounts of energy, often from fossil fuel-based sources. This contributes to the carbon footprint of EV manufacturing. Green manufacturing practices and innovations in battery technology are essential to reducing this impact.
Infrastructure Challenges
The need for widespread charging infrastructure is a barrier to EV adoption. Rural areas and underdeveloped regions often need more access to reliable charging stations, limiting the practicality of EVs.
Recycling Gaps
While battery recycling is improving, it needs to be more widespread. Scaling up recycling initiatives can significantly reduce the demand for raw materials and lower the environmental costs of EVs.
What Makes EVs Better for the Environment?
Sustainability Depends on Renewable Grids
EVs can only achieve their full environmental potential when powered by clean energy. Transitioning to renewable grids worldwide is key to maximizing their benefits.
Battery Recycling Is Essential
Recycling programs must be implemented globally to recover valuable materials, reduce waste, and minimize environmental damage.
Consumer Awareness and Behavior
Educating consumers about charging EVs with renewable energy and practicing sustainable habits can enhance the positive impact of EVs on the environment.
Government Support for Green Policies
Governments play a vital role in supporting EVs by incentivizing adoption and investing in infrastructure.
Conclusion
While EVs dramatically reduce tailpipe emissions and align with renewable energy goals, their full environmental benefits depend on clean electricity, sustainable production, and battery recycling. Governments, industries, and individuals must collaborate to address these challenges and unlock EVs’ true potential as a transformative solution to climate change.
FAQ’s
Are electric vehicles zero-emission vehicles?
Not entirely. While EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, the electricity used for charging and battery production contributes to emissions.
What makes EVs more sustainable than gasoline cars?
EVs reduce greenhouse gas emissions over their lifetime, especially when charged with renewable energy. They also eliminate harmful air pollutants.
What are the main challenges of EV adoption?
High production emissions, mining impacts, lack of infrastructure, and recycling gaps are key challenges.
How do governments encourage EV adoption?
Governments offer tax incentives subsidies, and invest in charging infrastructure to promote EVs and reduce emissions.
Can EVs help achieve climate goals?
Yes, EVs, when paired with renewable energy, play a critical role in reducing transportation emissions and transitioning to a low-carbon economy.